Fill Out a Valid Virginia State W 9 Template
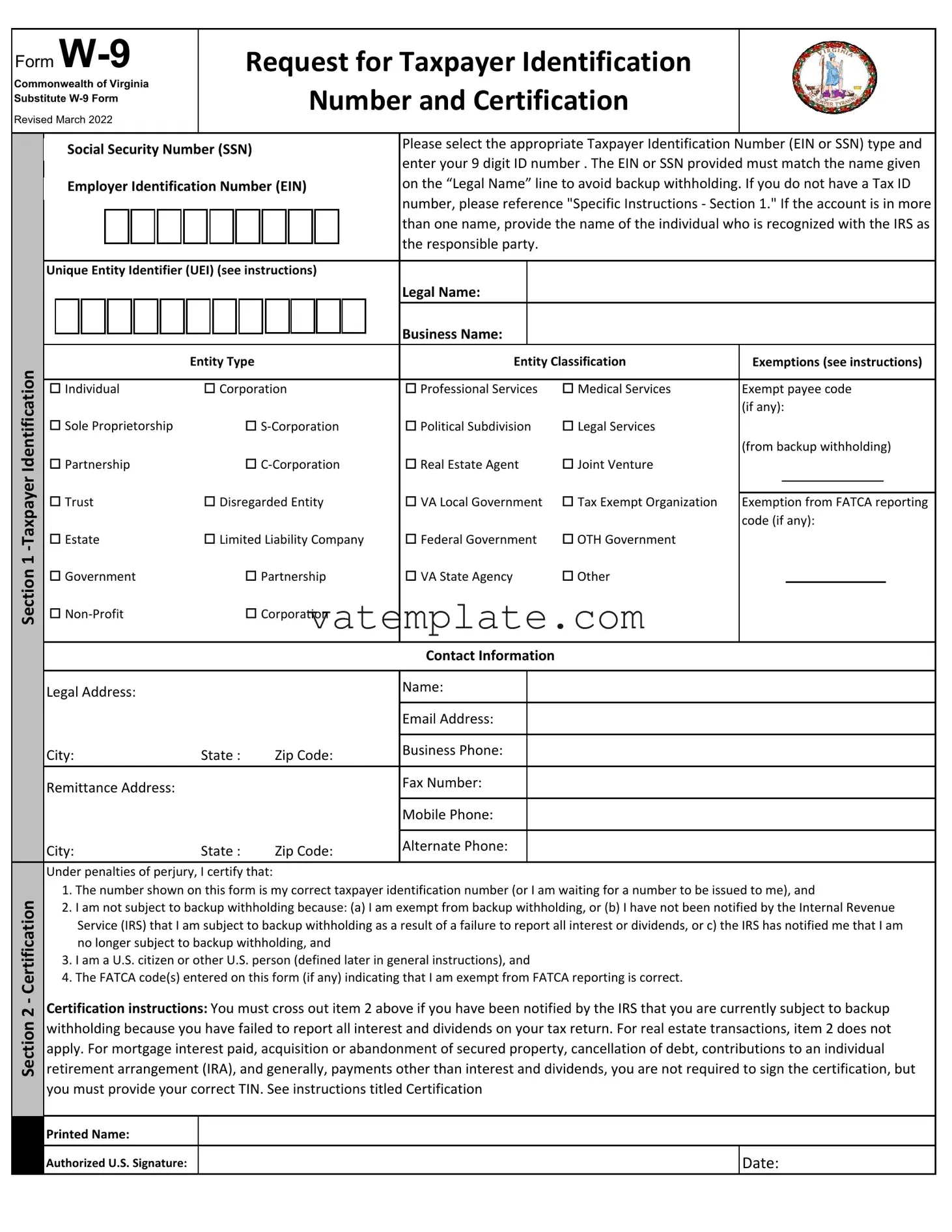
The Commonwealth of Virginia's Substitute W-9 Form is an essential document for individuals and entities engaging in business activities within the state, ensuring proper tax identification and certification. This revised document serves a pivotal role in maintaining tax compliance, providing a streamlined method for taxpayers to furnish their Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN), whether it be a Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN), in alignment with the name presented on the “Legal Name” line to preclude any backup withholding scenarios. It intricately outlines the necessity for a Dunn & Bradstreet Universal Numbering System (DUNS) number in certain cases, especially for those receiving federal grant funds, ensuring alignment with federal requirements. By incorporating selections for various entity types and classifications, from individual sole proprietors to corporations and non-profit organizations, this form accommodates a broad spectrum of taxpayers. It also emphasizes the significance of providing accurate contact information and legal address, reinforcing the importance of precise data submission. The form further delves into the exemptions applicable, elucidating scenarios where entities may be exempt from backup withholding and FATCA reporting, clearly articulating the criteria for such exemptions. The form concludes with a certification process, underscoring the necessity of affirming the accuracy of the information provided, the taxpayer's correct TIN, their status regarding backup withholding, and their qualification as a U.S. person or resident alien. This comprehensive document not only facilitates accurate tax reporting but also safeguards against potential penalties related to misinformation or non-compliance, making it an indispensable tool for conducting business within Virginia.
Virginia State W 9 Example

FORM |
|
|
|
|
Request for Taxpayer Identification |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Commonwealth of Virginia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number and Certification |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Substitute |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
REVISED March 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Social Security Number (SSN) |
Please select the appropriate Taxpayer Identification Number (EIN or SSN) type and |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Employer Identification Number (EIN) |
enter your 9 digit ID number . The EIN or SSN provided must match the name given |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
on the “Legal Name” line to avoid backup withholding. If you do not have a Tax ID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
number, please reference "Specific Instructions ‐ Section 1." If the account is in more |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
than one name, provide the name of the individual who is recognized with the IRS as |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the responsible party. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Unique Entity Identifier (UEI) (see instructions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legal Name: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Business Name: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Identification |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Entity Type |
Entity Classification |
Exemptions (see instructions) |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Partnership |
|
|
C‐Corporation |
Real Estate Agent |
Joint Venture |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Individual |
|
Corporation |
Professional Services |
Medical Services |
Exempt payee code |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(if any): |
||||
|
Sole Proprietorship |
|
|
S‐Corporation |
Political Subdivision |
Legal Services |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(from backup withholding) |
||||
‐Taxpayer |
Trust |
|
Disregarded Entity |
VA Local Government |
Tax Exempt Organization |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Exemption from FATCA reporting |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
code (if any): |
||||
|
Estate |
|
Limited Liability Company |
Federal Government |
OTH Government |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tionSec |
Government |
|
|
|
|
Partnership |
VA State Agency |
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
Non‐Profit |
|
|
|
|
Corporation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contact Information |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legal Address: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Email Address: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City: |
|
State : |
|
|
Zip Code: |
Business Phone: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remittance Address: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fax Number: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mobile Phone: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City: |
|
State : |
|
|
Zip Code: |
Alternate Phone: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Under penalties of perjury, I certify that: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
‐Certification2 |
|
1. The number shown on this form is my correct taxpayer identification number (or I am waiting for a number to be issued to me), and |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Certification instructions: You must cross out item 2 above if you have been notified by the IRS that you are currently subject to backup |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
2. I am not subject to backup withholding because: (a) I am exempt from backup withholding, or (b) I have not been notified by the Internal Revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Service (IRS) that I am subject to backup withholding as a result of a failure to report all interest or dividends, or c) the IRS has notified me that I am |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
no longer subject to backup withholding, and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
3. I am a U.S. citizen or other U.S. person (defined later in general instructions), and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Section |
|
4. The FATCA code(s) entered on this form (if any) indicating that I am exempt from FATCA reporting is correct. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
retirement arrangement (IRA), and generally, payments other than interest and dividends, you are not required to sign the certification, but |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
withholding because you have failed to report all interest and dividends on your tax return. For real estate transactions, item 2 does not |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
apply. For mortgage interest paid, acquisition or abandonment of secured property, cancellation of debt, contributions to an individual |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
you must provide your correct TIN. See instructions titled Certification |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Printed Name: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Authorized U.S. Signature: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If you are a nonresident alien or a foreign entity, give the requester the appropriate completed Form
What is backup withholding? Persons making certain payments to you must under certain conditions withhold and pay to the IRS a percentage of such payments. This is called “backup withholding.” Payments that may be subject to backup withholding include interest,
You will not be subject to backup withholding on payments you receive if you give the requester your correct TIN, make the proper certifications, and report all your taxable interest and dividends on your tax return.
Payments you receive will be subject to backup withholding if:
1.You do not furnish your TIN to the requester,
2.You do not certify your TIN when required (see Section 2 Certification for details),
3.The IRS tells the requester that you furnished an incorrect TIN,
4.The IRS tells you that you are subject to backup withholding because you did not report all your interest and dividends on your tax return (for reportable interest and dividends only), or
5.You do not certify to the requester that you are not subject to backup withholding under 4 above (for reportable interest and dividend accounts opened after 1983 only).
Certain payees and payments are exempt from backup withholding.
What is FATCA reporting? The Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) requires a participating foreign financial institution to report all United States account holders that are specified United States persons. Certain payees are exempt from FATCA reporting.
Updating Your Information
You must provide updated information to any person to whom you claimed to be an exempt payee if you are no longer an exempt payee and anticipate receiving reportable payments in the future from this person. For example, you may need to provide updated information if you are a C corporation that elects to be an S corporation, or if you no longer are tax exempt. In addition, you must furnish a new
Form
Penalties
Failure to furnish TIN. If you fail to furnish your correct TIN to a requester, you are subject to a penalty of $50 for each such failure unless your failure is due to reasonable cause and not to willful neglect.
Civil penalty for false information with respect to withholding. If you make a false statement with no reasonable basis that results in no backup withholding, you are subject to a $500 penalty.
Criminal penalty for falsifying information. Willfully falsifying certifications or affirmations may subject you to criminal penalties including fines and/or imprisonment.
Misuse of TINs. If the requester discloses or uses TINs in violation of federal law, the requester may be subject to civil and criminal penalties.
Specific Instructions
Section 1
Check the appropriate Tax Identification Number (TIN) type. Enter your EIN/SSN in the space provided. If you are a resident alien and you do not have and /or are not eligible to get an SSN, your TIN is your IRS individual taxpayer identification number (ITIN). Enter it in the social security number box. If you do not have an ITIN, see How to get a TIN below.
Number (SSN)" box and enter the SSN of the sole proprietor.
e.If you are a
Note: If an LLC has one owner, the LLC's default tax status is "disregarded entity". If an LLC has two owners, the LLC's default tax status is "partnership". If an LLC has elected to be taxed as a corporation, it must file IRS Form 2553 (S Corporation) or IRS Form 8832 (C Corporation).
Vendors are requested to enter their Unique Entitiy Identifier Number (UEI), if applicable. See number requirement below.
Unique Entity Identifier (UEI) number requirement. The
United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) requires all vendors that receive federal grant funds have their UEI number recorded with and subsequently reported to the granting agency. If your entity is registered in SAM.gov today, your Unique Entity ID (UEI) has already been assigned and is viewable in SAM.gov
Legal Name. If you are an individual, you must generally enter the name shown on your social security card. However, if you have changed your last name, for instance, due to marriage without informing the Social Security Administration of the name change, enter your first name, the last name shown on your social security card, and your new last name. If the account is in joint names, list first and then circle the name of the person or entity whose number you enter in Part I of the form. If you are using a name other than that which is listed on a Social Security Card, please enter the legal entity name as filed with the IRS. In general, enter the name shown on your income tax return. Do not enter a Disregarded Entity Name on this line.
Business Name. Business, Disregarded Entity, trade, or DBA ("doing business as") name.
Entity Type. Select the appropriate entity type.
Sole proprietor. Enter your individual name as shown on your social security card on the “Legal Name” line. You may enter your business, trade, or “doing business as (DBA)” name on the “Business Name” line.
Partnership. A partnership is an entity reflecting a relationship existing between two or more persons who join to carry on a trade or business. Enter the partnerships entity's name on the "Legal Name" line. This name should match the name shown on the legal document creating the entity. You may enter your business, trade, or "doing business as (DBA) name on the "Business Name" line.
Trust. A legal entity that acts as fiduciary, agent or trustee on behalf of a person or business entity for the purpose of administration, management and the eventual transfer of assets to a beneficial party. Enter the name of the legal entity on the "Legal Name" line.
Estate. A separate legal entity created under state law solely to transfer property from one party to another. The entity is separated by law from both the grantor and the beneficiaries. Enter the name of the legal entity on the "Legal Name" line.
Corporation. A company recognized by law as a single body with its own powers and liabilities, separate from those of the individual members. Enter the entity's name on the "Legal Name" line and any trade or "doing business as (DBA)" name on the "Business Name" line.
Corporations are exempt from backup withholding for certain payments, such as interest and dividends. Corporations are not exempt from backup withholding for payments made in settlement of payment card or third party network transactions.
Note. If you are exempt from backup withholding, you should still complete this form to avoid possible erroneous backup withholding.
The following codes identify payees that are exempt from backup withholding:
1 - An organization exempt from tax under section 501(a), any IRA, or a custodial account under section 403(b)(7) if the account satisfies the requirements of section 401(f)(2)
2 - The United States or any of its agencies or instrumentalities 3 - A state, the District of Columbia, a possession of the United States, or any of their political subdivisions, agencies, or instrumentalities
4 - A foreign goverenemtn or any of its political subdivisions, agencies, or instrumentalities
5 - A corporation
6 - A dealer in securities or commodities required to register in the United States, the District of Columbia, or a possession of the United States
7 - A futures commission merchant registered with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission
8 - A real estate investment fund
9 - An entity registered at all times during the tax year under the Investment Company Act of 1940
10- A common trust fund operated by a bank under section 584(a)
11 - A financial institution
12 - A middleman known in the investment community as a nominee or custodian
13 - A trust exempt from tax under section 664 or described in section 4947.
The following chart shows types of payments that may be exempt from backup withholding. The chart applies to the exempt payees listed above, 1 through 13.
IF the payment is for. . . THEN the payment is exempt for. . .
Interest and dividend |
All exempt payees except for 7 |
payments |
|
Broker transactions |
Exempt payees 1 through 4 and 6 |
|
through 11 and all C corporations. |
|
S corporations must not enter an |
|
exempt payee code because they |
|
are exempt only for sales of |
|
noncovered securities acquired prior |
|
to 2012. |
Barter exchange |
Exempt payees 1 through 4 |
transactions and |
|
patronage dividends |
|
Payments over $600 |
Generally, exempt payees 1 through |
required to be reported |
52 |
and direct sales over |
|
$5,0001 |
|
Payments made in |
Exempt payees 1 through 4 |
settlement of payment |
|
card or third party |
|
network transactions |
|
1See Form
2However, the following payments made to a corporation and reportable on Form
Exemption from FATCA reporting code. The following codes identify payees that are exempt from reporting under FATCA. These codes apply to persons submitting this form for accounts maintained outside of the United States by certain foreign financial institutions. Therefore, if you are only submitting this form for an account you hold in the United States, you may leave this field blank. Consult with the person requesting this form if you are uncertain if the financial
How to get a TIN. If you do not have a TIN, apply for one immediately. To apply for an SSN, get Form
If you do not have a TIN, write “Applied For” in the space for the TIN, sign and date the form, and give it to the requester. For interest and dividend payments, and certain payments made with respect to readily tradable instruments, generally you will have 60 days to get a TIN and give it to the requester before you are subject to backup withholding on payments. The
Enter the TIN which coincides with the 'Legal Name' provided on the form.
a.If you are an individual, check the "Social Security Number (SSN)" box and enter the SSN.
b.If you are a Grantor or Revocable Trust, check the "Social Security Number (SSN)" box and enter the SSN of the Grantor.
c. If you are a Resident Alien, check the "Social Security Number (SSN)" box and enter your SSN or your ITIN (IRS Individual Taxpayer Identification Number).
d.If you are a Sole Proprietor, check the "Social Security
business as (DBA)" name on the "Business Name" line.
Limited liability company (LLC). An LLC with at least two members is classified as a partnership for federal income tax purposes unless it files Form 8832 and affirmatively elects to be treated as a corporation. Enter the name of the partnership or corporation. An LLC with only one member is treated as an entity disregarded as separate from its owner for income tax purposes (but as a separate entity for purposes of employment tax and certain excise taxes), unless it files Form 8832 and affirmatively elects to be treated as a corporation. If you are a
Contact Information. Enter your contact information.
Enter your Legal Address. Enter your Remittance Address. A Remittance Address is the location in which you or your entity receives business payments.
Enter your Business Phone Number. Enter your Mobile Phone Number, if applicable. Enter your Fax Number, if applicable. Enter your Email Address.
For clarification on any of the fields, see www.irs.gov.
Exemptions
If you are exempt from backup withholding and/or FATCA reporting, enter in the Exemptions box, any code(s) that may apply to you. See Exempt payee code and Exemption from FATCA reporting code.
Exempt payee code. Generally, individuals (including sole proprietors) are not exempt from backup withholding.
institution is subject to these requirements.
A - An organization exempt from tax under section 501(a) or any individual retirement plan as defined in section 7701(a)(37)
B - The United States or any of its agencies or instrumentalities C - A state, the District of Columbia, a possession of the United States, or any of their political subdivisions or instrumentalities
D - A corporation in the stock of which is regularly traded on one or more established securities markets, as described in Reg. section
E - A corporation that is a member of the same expanded affiliated group as a corporation described in Reg. section
F - A dealer in securities, comodities, or derivative financial instruments (including notional principal contracts, futures, forwards, and options) that is registered as such under teh laws of the United States or any state
G - A real estabte investement trust
H - A regulated investment company as defined in section 851 or an entity registered at all times during the tax year under the Investment Company Act of 1940
I - A common trust fund as defined in section 584(a) J - A bank as defined in section 581
K - A broker
L - A trust exempt from tax under section 664 or described in section 4947(a)(1)
M - A tax exempt trust under a section 403(b) plan or section 457(g) plan
Section 2 - Certification
To establish to the paying agent that your TIN is correct, you are not subject to backup withholding, or you are a U.S. person, or resident alien, sign the certification on Form
For a joint account, only the person whose TIN is shown in Part I should sign (when required).
Form Properties
| Fact | Detail |
|---|---|
| Form Purpose | The Virginia State W-9 form is used to provide Taxpayer Identification Number and certification. |
| Revised Date | The form was revised in 2021. |
| Applicability | It applies to individuals and entities to avoid backup withholding. |
| Tax Identification Numbers | Includes options for Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN). |
| Legal Name Requirement | The legal name provided must match the TIN to prevent withholding issues. |
| Entity Types | Covers a range of entities including Individual, Corporation, Sole Proprietorship, and more. |
| Exemptions | Sections are provided for indicating exemptions from backup withholding or FATCA reporting. |
| DUNS Number | Request for Dunn & Bradstreet Universal Numbering System (DUNS) for entities receiving federal funds. |
| Signature Requirement | Must be signed under penalties of perjury certifying the accuracy of the information provided. |
| Governing Law | The form is governed by the Internal Revenue Code and applicable Virginia state laws. |
Steps to Filling Out Virginia State W 9
Once you've received the Virginia State W-9 Form, it's important to complete it accurately to ensure timely and efficient processing. This form requests your Taxpayer Identification Number and certification, crucial for tax purposes and to potentially avoid backup withholding. The steps below are designed to help you fill out the form properly.
- At the top of the form, select either your Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN) by checking the appropriate box. Then, fill in the 9-digit number in the spaces provided.
- Under "Legal Name", enter your name as it appears on your income tax return.
- If you have a Business Name (also known as a Doing Business As), input it in the respective field.
- Select your Entity Type by checking the corresponding box that accurately represents your tax status (e.g., Individual, Corporation, Sole Proprietorship, etc.).
- In the Entity Classification section, mark the category that best describes your entity's classification (e.g., S-Corporation, Partnership).
- If applicable, fill in your Dunn & Bradstreet Universal Numbering System (DUNS) number.
- Under Exemptions, note any codes that apply to you if you are exempt from FATCA reporting or backup withholding as per the instructions provided on the form.
- Provide your Contact Information, filling out your legal address, remittance address (if different), telephone number, fax number, and email address.
- Review the Certification section carefully. If everything is correct and you agree, cross out item 2 under Certification only if it applies to you, then sign and date the form. If you are not subject to backup withholding, no cross-out is needed.
- Finally, mail or deliver your completed W-9 form to the address provided by the requester or the instructions on the form layout. This is usually towards the Commonwealth Vendor Group or the specific department that requested the form from you.
By following these steps, you're ensuring that your information is accurately conveyed and you're compliant with tax reporting requirements. It's always a good idea to keep a copy of the completed form for your records. Should your information change in the future, such as your address or entity status, you'll need to submit a new W-9 form reflecting these updates.
FAQ
What is a Virginia State W-9 Form?
The Virginia State W-9 Form, officially known as the Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification, is a document used by the Commonwealth of Virginia. It's similar to the federal Form W-9 and is used to provide your correct taxpayer identification number (TIN) to entities that are required to file information returns with the IRS on your behalf. This could include reports of income paid to you, real estate transactions, or other financial interactions that need to be reported to the IRS.
When do I need to complete the Virginia State W-9 Form?
You need to complete the Virginia State W-9 Form anytime you are initiating or conducting business with an entity that requires your Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) for reporting purposes to the IRS. This often includes employers, financial institutions, and government agencies in Virginia. The form serves as a certification of your TIN, whether it's your Social Security Number (SSN) for individuals or an Employer Identification Number (EIN) for businesses.
What information do I need to provide on the Virginia State W-9 Form?
The main pieces of information you need to provide on the Virginia State W-9 Form include:
- Your legal name as recognized by the IRS
- Your TIN, which can be either your SSN or your EIN
- The type of entity you are, such as individual, corporation, partnership, etc.
- Your business name (if different from your legal name)
- Your contact information, including address, phone number, and email
- Certification that the information you are providing is correct
Am I subject to backup withholding if I don’t fill out the Virginia State W-9 Form correctly?
Yes, if you do not correctly fill out the Virginia State W-9 Form, or if you do not provide the form at all, you may be subject to backup withholding. Backup withholding is a way for the IRS to ensure they collect the necessary tax on income where tax reporting might otherwise be evaded. If you’re subject to backup withholding, the entity paying you will withhold taxes from your payment at the current rate and send this money to the IRS on your behalf.
How do I know if I am exempt from backup withholding and/or FATCA reporting?
There are specific categories of payees that are exempt from backup withholding and FATCA reporting. For example, corporations (in certain circumstances), tax-exempt organizations, and government entities are often exempt. To claim an exemption, you need to review the instructions provided with the Virginia State W-9 Form. If you qualify, you should indicate your exempt status in the relevant section of the form. It's important to consult with a tax professional if you are unsure about your exemption status.
Where do I send my completed Virginia State W-9 Form?
After you have completed and signed your Virginia State W-9 Form, you will typically send it to the requester and not directly to the IRS or any state tax agency. The requester, such as an employer or a bank, needs this information to accurately report transactions to the IRS under your TIN. If you are unsure where to send the completed form, contact the entity requesting it for instructions.
Common mistakes
When completing the Virginia State W-9 Form, there are common mistakes that individuals and businesses often make. Identifying and avoiding these errors can streamline the process, ensuring compliance and timely handling of your form. Below are seven typical mistakes:
Selecting the incorrect Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) type: One must choose the right TIN type (EIN or SSN) and ensure it matches the legal name provided.
Entering an incorrect TIN: The 9-digit TIN entered must be accurate and correspond with the IRS records for the individual or entity.
Failing to provide the legal name: The legal name should match what is on file with the IRS for the TIN provided. For individuals, it should match the name on your Social Security card.
Omitting the business name: If operating under a business name, DBA, or trade name, this field should not be left blank.
Incorrect entity type selection: The entity type should reflect the classification of the business according to IRS records.
Not indicating exemptions correctly: If exempt from backup withholding or FATCA reporting, the proper exemption code must be entered.
Signature and date omissions: The form must be signed and dated to certify the accuracy of the information provided, indicating agreement to the conditions stated on the form.
Ensuring accurate and complete information when filling out the Virginia State W-9 Form helps prevent unnecessary delays or issues with tax reporting. Paying careful attention to the details can save time and reduce the risk of complications with the IRS.
Documents used along the form
When businesses and individuals engage in transactions with the Commonwealth of Virginia, often they are required to complete a Virginia State W-9 form. This form is crucial for providing taxpayer identification and certification information to the state. Along with the Virginia State W-9 form, there are several other documents that entities might find themselves needing to submit or update for a complete and compliant financial relationship with various government agencies. By understanding the importance and usage of each form, entities can ensure smoother operations and compliance with tax and reporting standards.
List of forms and documents commonly used alongside the Virginia State W-9 Form:- Form 1099-MISC: This document is essential for reporting payments made to independent contractors, attorney fees, and other payments for services rendered by non-employees. It's especially relevant for businesses that hire freelancers or outside firms.
- Form W-4: Commonly used by employees to indicate their tax withholding preferences. Though not directly related to the W-9, employers might need to differentiate between independent contractors and employees for tax reporting purposes.
- Virginia Contractor's Certificate for Worker's Compensation: This form is critical for contractors operating in Virginia, confirming they meet the state's workers' compensation insurance requirements. It's a necessary aspect of maintaining a lawful and safe working environment.
- Business Registration Certificate: In Virginia, businesses must register with the Virginia Department of Taxation. This registration is vital for tax compliance and is a separate process from the federal identification required on a W-9.
In conclusion, understanding each of these documents' role and how they complement the information on the Virginia State W-9 form can significantly aid in maintaining proper tax and legal standing. Businesses, especially, must be diligent in keeping these documents current and accurately filled out to prevent any disruptions in their operations or compliance with state and federal laws.
Similar forms
The Virginia State W-9 form is similar to the federal IRS W-9 form, Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification. This form is commonly used by individuals and entities to provide their correct taxpayer identification number (TIN) to entities that will pay them income, ensuring accurate tax reporting to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Both forms serve a comparable purpose: to gather information from vendors, contractors, or other payees to facilitate the proper reporting of taxes. They request similar pieces of information, such as the payee's legal name, tax classification, TIN (which could be a Social Security Number for individuals or an Employer Identification Number for entities), and certification that the information provided is accurate to avoid backup withholding.
Another document the Virginia State W-9 form is akin to is the Form W-8 series, which includes Form W-8BEN, Form W-8BEN-E, Form W-8ECI, Form W-8EXP, and Form W-8IMY. These forms are utilized by foreign entities or non-resident aliens to certify their status and claim exemption from certain U.S. taxes under tax treaties, or to claim that they are effectively connected with a U.S. business and therefore subject to taxation. While the W-9 form is for U.S. persons (including citizens and entities), the W-8 forms apply to non-U.S. persons. Both sets of forms are used to determine the correct tax reporting status but are directed at different populations with respect to U.S. tax laws.
Comparably, the Virginia State W-9 form also resembles the Substitute Form W-9 that many states and organizations may employ. Substitute W-9 forms are customized versions of the federal W-9 form created by individual states, businesses, or institutions to meet specific requirements. These substitute forms still collect taxpayer identification information for tax reporting and backup withholding purposes. They must adhere to certain IRS specifications but can also include additional requests relevant to the organization's needs, such as vendor information or procurement specifics. Thus, while the core purpose and content align closely with the federal W-9 form, substitute forms can offer tailored approaches to tax information collection.
Dos and Don'ts
When completing the Virginia State W-9 form, it is crucial to adhere to certain dos and don'ts to ensure accuracy and compliance with regulations.
Things You Should Do:
- Ensure the Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) provided matches the "Legal Name" on the form to prevent backup withholding issues.
- If you do not have a TIN, apply for one immediately and temporarily write "Applied For" in the space provided. However, remember to update the form once you receive your TIN.
- Meticulously check the appropriate boxes that accurately reflect your Entity Type and Entity Classification. This is crucial for proper documentation and verification purposes.
- Sign and date the form in the certification section to attest that the information provided is accurate and you are aware of the conditions that apply regarding backup withholding and FATCA reporting.
Things You Shouldn't Do:
- Do not leave any required fields blank. Incomplete forms may lead to processing delays or incorrect filing of your tax information.
- Avoid using a TIN that does not match the legal name or entity listed on the form. This mismatch can lead to unnecessary confusion and potential legal complications.
- Do not forget to update your information on the form if your TIN, legal name, or entity status changes at any point. Keeping your W-9 current helps avoid potential withholding or compliance issues.
- Resist the temptation to provide false information. Willfully falsifying certifications or failing to provide a TIN can lead to penalties, including fines and imprisonment.
Following these guidelines will help ensure that your submission of the Virginia State W-9 form is compliant, accurate, and devoid of any issues that might complicate your tax standing or relationship with entities requiring this form.
Misconceptions
There are several common misconceptions about the Virginia State W-9 form that need to be clarified to ensure accurate and compliant submissions. Understanding these aspects can help individuals and entities provide the correct information and avoid potential issues with tax reporting and backup withholding.
- Misconception 1: The Virginia State W-9 form is different from the federal W-9 form.
While the Virginia State W-9 form serves a similar purpose as the federal W-9 form—to provide taxpayer identification information—it is specifically designed for use within the Commonwealth of Virginia. Entities or individuals conducting business with Virginia state agencies are often required to complete this form.
- Misconception 2: Only businesses need to complete the Virginia State W-9 form.
Both individuals and entities, including sole proprietors, corporations, partnerships, and nonprofits, might be required to submit a Virginia State W-9 form, depending on their transactions with Virginia state agencies.
- Misconception 3: You need to have a business to have an Employer Identification Number (EIN) for the W-9.
While businesses commonly use an EIN, certain individuals, such as sole proprietors or those with employees, may also have an EIN and should provide this number on the W-9 form if applicable.
- Misconception 4: The Legal Name and Business Name should always match.
The "Legal Name" should match the name associated with the taxpayer identification number provided. An individual may list their name as the legal name and their business name as applicable, especially if operating under a "doing business as" (DBA) name.
- Misconception 5: The form is only for reporting purposes and has no impact on backup withholding.
Incorrectly completing the Virginia State W-9 form or failing to provide it when requested can result in backup withholding. It's important to accurately fill out and submit the form to prevent unnecessary withholding.
- Misconception 6: Non-U.S. residents do not need to complete the Virginia State W-9 form.
Non-U.S. residents who conduct business with Virginia state agencies may be required to complete the form. However, they might need to submit additional documentation to support their foreign status and claim exemption from certain U.S. taxes.
Correctly understanding the Virginia State W-9 form requirements ensures compliance with tax laws and facilitates smoother transactions with state agencies. Always consult with a tax professional if you have questions about your specific situation.
Key takeaways
Filling out the Virginia State W-9 Form is a crucial step for individuals and entities conducting business in Virginia, ensuring compliance and proper tax treatment. Here are six key takeaways to keep in mind:
- Choose the Correct TIN: It's essential to select the appropriate Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) type and ensure it matches the name given on the “Legal Name” line to avoid issues such as backup withholding.
- Legal Name and Business Name: For individuals, the legal name should match what's on your social security card, whereas businesses should use the name registered with the IRS. A separate line is provided for DBA (Doing Business As) names.
- Entity Type Matters: Clearly indicating whether you’re operating as an individual, sole proprietorship, corporation, partnership, etc., is vital. This choice affects how you're taxed and what liabilities you may face.
- Contact Information: Ensure your contact information, including your legal and remittance addresses, email, and phone numbers, is current. This helps avoid delays or issues in communication.
- Exemptions Can Apply: If you’re exempt from backup withholding or FATCA reporting, be sure to indicate this by entering the appropriate exemption codes on the form.
- Signature and Certification: Signing the form certifies that the information provided is accurate and that you are a U.S. person (including a resident alien). This is a declaration made under the penalties of perjury, highlighting the importance of providing accurate information.
Remember, the purpose of the Form W-9 is to provide your correct TIN to the person requesting it and to certify your tax status. Filling out this form accurately is fundamental to ensure you comply with U.S. tax laws and avoid potential penalties.
Other PDF Forms
How to Get Towing License - It’s important for applicants to keep a copy of the completed form for their records.
501c3 Virginia - This document reassures handicapped individuals that the state supports their right to enhanced mobility through financial incentives.
Wv Divorce Papers - Attach a brief explanation if the judgment does not meet the criteria for a final decision.